|
Canku Ota
|
 |
|
(Many Paths)
|
||
|
An Online Newsletter
Celebrating Native America
|
||
|
February 2018 - Volume
16 Number 2
|
||
|
|
||
|
Infant Skeleton Sheds
New Llight On Early Native American Populations
|
||
|
by ZME Science newsletter
|
||
|
The remains of a six-week-old infant cast new light upon the Native American founding population. Scientists divided the ancient American populations into two categories: the Southern and the Northern Native Americans. The two groups are related, but a link between them and an ancient Siberian population was missing, until now.
Researchers named this population "Ancient Beringians" after Beringia, the land bridge that connected northeast Asia with northwestern North America, during the Pleistocene epoch — sometimes called the Ice Age.
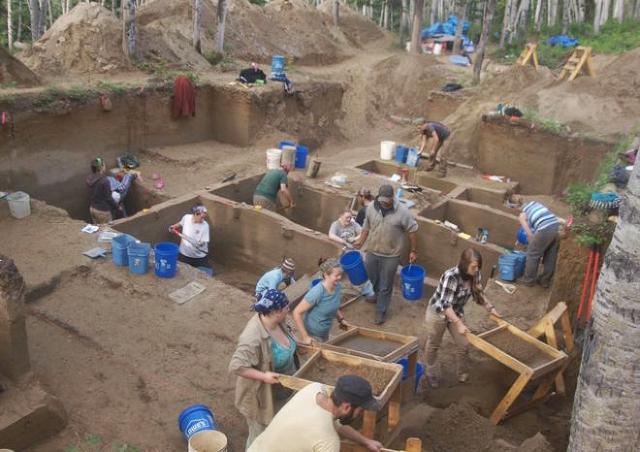
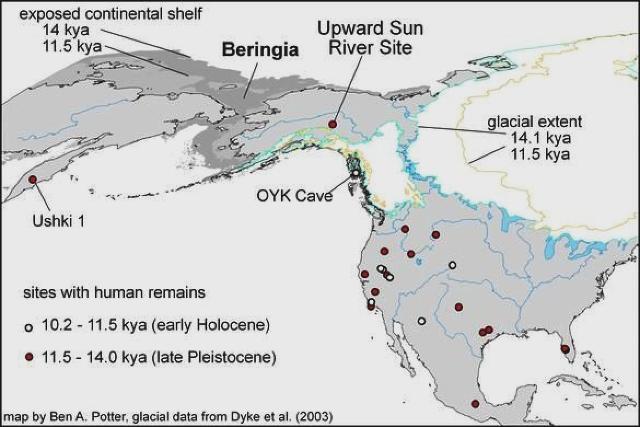
The girl was named Xach'itee'aanenh t'eede gaay, or Sunrise Child-girl, by the local Native community. Her skeleton was discovered at the Upward Sun River archaeological site in Alaska in 2013. Scientists say the child lived 11,500 years ago, long after the first wave of migration occurred, but her genome was consistently different from the two types of ancient Native Americans.
This is the first ancient skeleton ever discovered in Alaska — acidic soils make bone tissue and DNA preservation very difficult.
The Northern and the Southern branches are thought to have separated somewhere between 17,000-14,000 years ago. The two groups probably went separate ways as they passed through or around the Cordilleran and Laurentide ice sheets that covered present-day Canada and a part of northern United States. Scientists believe that the Ancient Beringians were left behind the ice sheets and remained in Alaska. Next, the population was absorbed by other Native groups derived from the Northern branch, that migrated back after the ice had melted away.
The paper was published in the Nature journal on the 3rd of January 2018.
Arctic
Research Consortium of the United States (ARCUS) |
||||||
Map of excavation site of early human remains in North America.
Image courtesy of Ben A. Potter.
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Canku Ota is a free Newsletter celebrating Native America, its traditions and accomplishments . We do not provide subscriber or visitor names to anyone. Some articles presented in Canku Ota may contain copyright material. We have received appropriate permissions for republishing any articles. Material appearing here is distributed without profit or monetary gain to those who have expressed an interest. This is in accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107. | ||
|
Canku Ota is a copyright ©
2000 - 2018 of Vicki Williams Barry and Paul Barry.
|
||
 |
 |
|
|
The "Canku
Ota - A Newsletter Celebrating Native America" web site and
its design is the
|
||
|
Copyright ©
1999 - 2018 of Paul C. Barry.
|
||
|
All Rights Reserved.
|
||