|
Canku Ota
|
 |
|
(Many Paths)
|
||
|
An Online Newsletter
Celebrating Native America
|
||
|
December 2015 - Volume
13 Number 12
|
||
|
|
||
|
BASIC FACTS ABOUT
BLACK BEARS
|
||
|
by Defenders of Wildlife
|
||
Black bear fur is usually a uniform color except for a brown muzzle and light markings that sometimes appear on their chests. Eastern populations are usually black in color while western populations often show brown, cinnamon, and blond coloration in addition to black. Black bears with white-bluish fur are known as Kermode (glacier) bears and these unique color phases are only found in coastal British Columbia, Canada. Diet
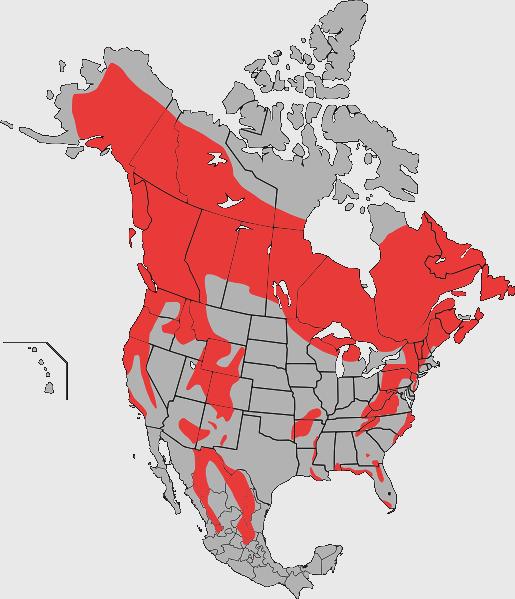
Population Range Behavior Black bears tend to be solitary animals, with the exception of mothers and cubs. The bears usually forage alone, but will tolerate each other and forage in groups if there is an abundance of food in one area. Most black bears hibernate depending on local weather conditions and availability of food during the winter months. In regions where there is a consistent food supply and warmer weather throughout the winter, bears may not hibernate at all or do so for a very brief time. Females give birth and usually remain denned throughout the winter, but males and females without young may leave their dens from time to time during winter months.
Reproduction
|
|||||
American Black Bear Range
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Canku Ota is a free Newsletter celebrating Native America, its traditions and accomplishments . We do not provide subscriber or visitor names to anyone. Some articles presented in Canku Ota may contain copyright material. We have received appropriate permissions for republishing any articles. Material appearing here is distributed without profit or monetary gain to those who have expressed an interest. This is in accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107. | ||
|
Canku Ota is a copyright ©
2000 - 2015 of Vicki Williams Barry and Paul Barry.
|
||
 |
 |
|
|
The "Canku
Ota - A Newsletter Celebrating Native America" web site and
its design is the
|
||
|
Copyright ©
1999 - 2015 of Paul C. Barry.
|
||
|
All Rights Reserved.
|
||